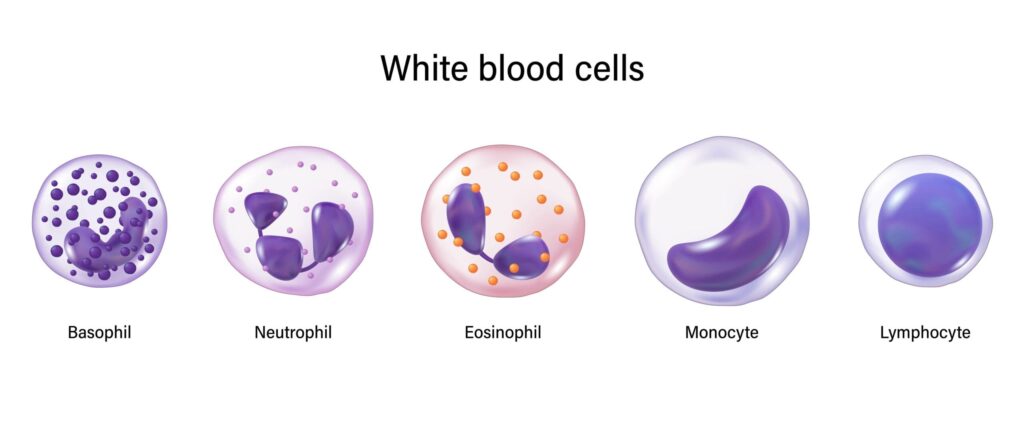
White Blood cells (WBC) are the body’s main defenders against infections, viruses, bacteria, and foreign agents.
| Group | Reference range (×10⁹/L) |
|---|---|
| Adults | 4.0 – 9.0 |
| Children | 5.0 – 15.0 |
| Newborns | 9.0 – 30.0 |
| Pregnant women | Up to 10–15 (physiological increase) |
Note: References may vary slightly in laboratories.
Reasons:
Symptoms:
Reasons:
Symptoms:
Depend on the reason:
Important!