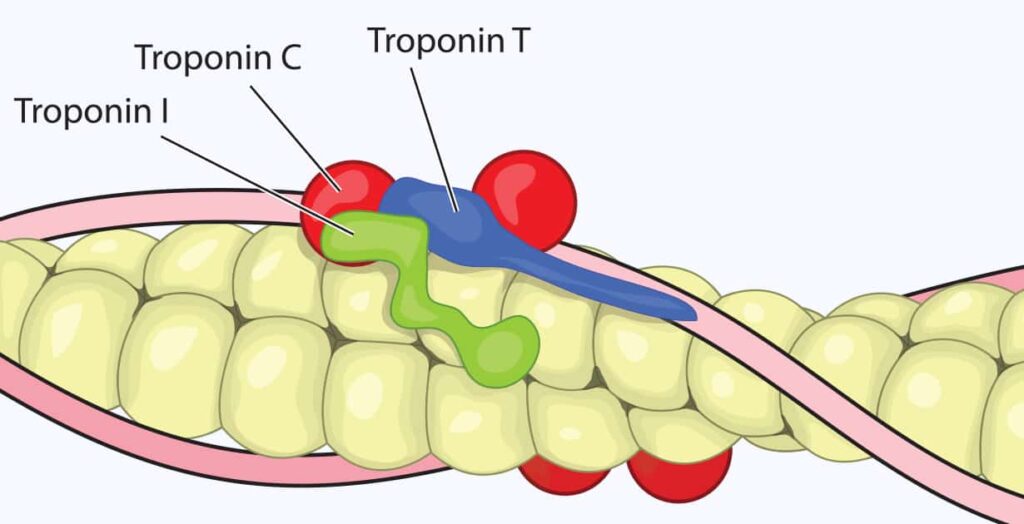
Troponin I (cTnI) is a key biomarker of myocardial damageand is part of the contractile system of the heart muscle. Normally, it is practically not detected in the blood.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Healthy adults | <0.04 ng/mL |
| Myocardial infarction threshold | >0.5 ng/mL (with rising trend) |
| “Grey zone” | 0.04–0.5 ng/mL (repeat testing required in 3–6 hours) |
Note: References depend on the analysis method. In the elderly, a slight increase is acceptable (up to 0.1 ng / ml).
Situations:
It has no clinical significance.
Critical level:
Main reasons:
Symptoms:
Important: