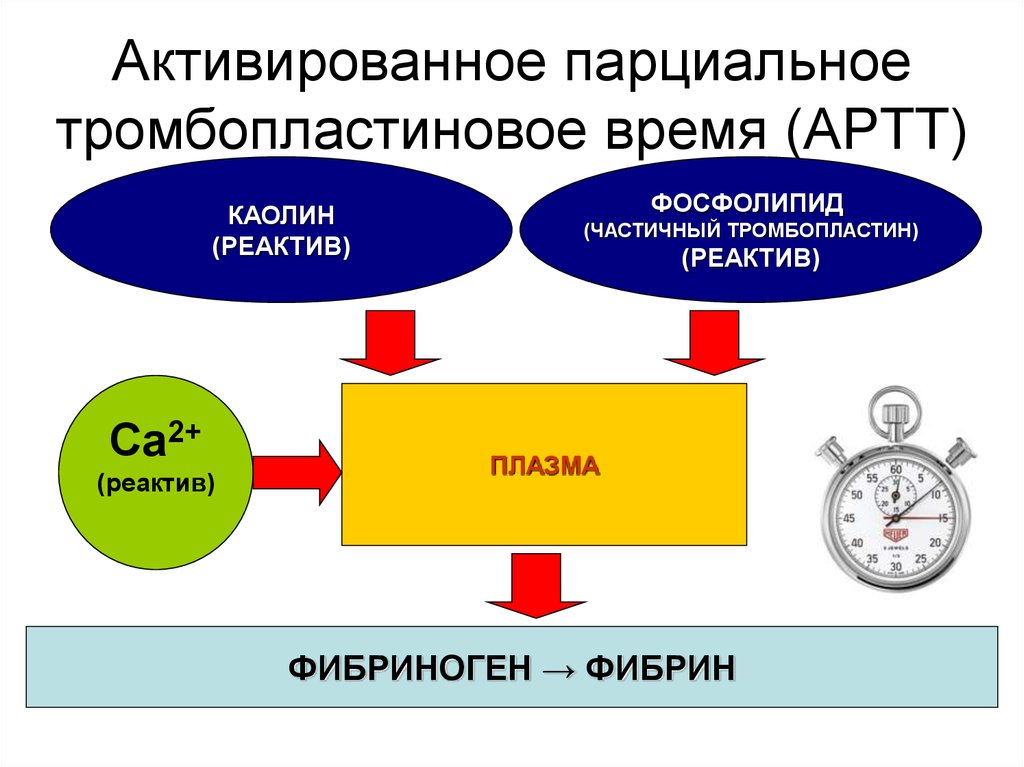
Thrombin time is an indicator that reflects the rate of conversion of fibrinogenFibrinogen is a protein, one of the main blood clotting factors. It is necessary for the formation of blood clots and stopping bleeding, helps in healing damaged tissues and restoring their blood supply. When the wall of a vessel of any caliber is damaged, a cascade of biochemical reactions is triggered in the blood, the final stage of which is the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin. A blood clot is formed. Fibrinogen is synthesized by liver cells and is constantly present in the blood at a certain concentration. to fibrinFibrin is an insoluble protein substance formed during blood clotting and precipitating as a tangle of threads. under the action of thrombin. This test evaluates the final stage of blood clotting and helps identify disorders in the hemostatic system associated with:
Standards may vary slightly from laboratory to laboratory, but usually:
If the time is increased , folding is slowed down, and if it is reduced , it is accelerated.
Reasons:
Symptoms:
Reasons:
Symptoms:
To clarify the diagnosis, you can prescribe:
If you have any abnormalities in the analysis, it is important to consult a hematologist or therapist for further examination.