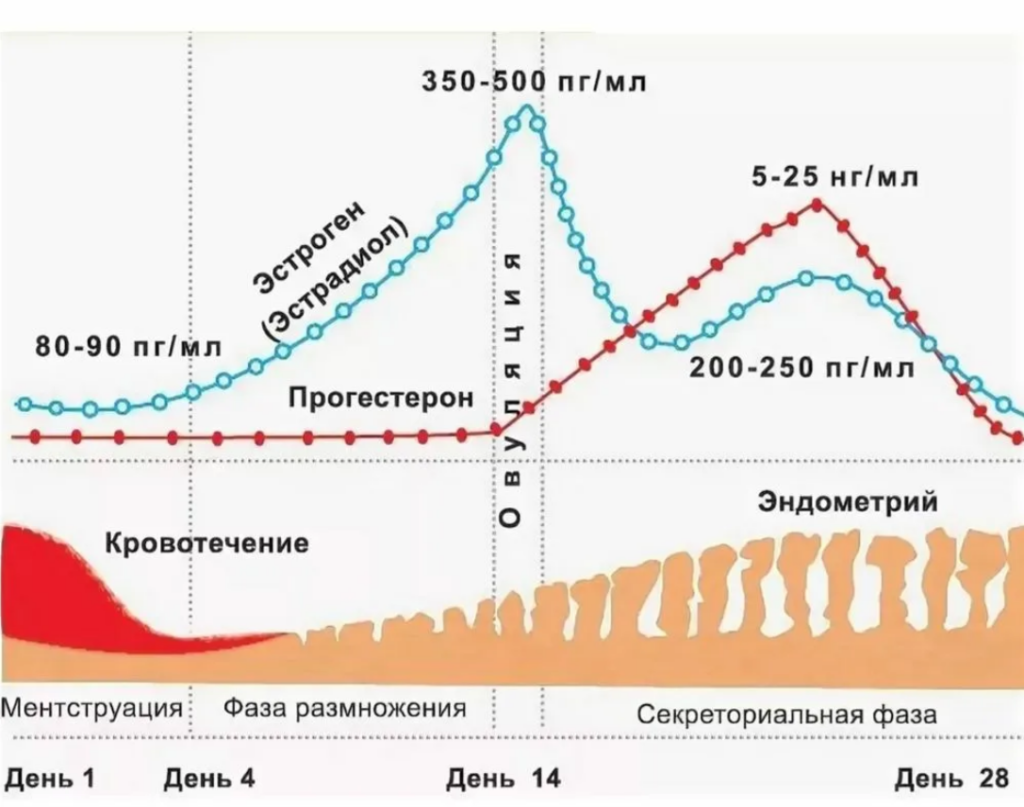
Estradiol is the main estrogen produced in the ovaries (follicles), as well as in the adrenal glands and adipose tissue.
Functions:
✔ Regulation of the menstrual cycle -stimulates the growth of the endometrium.
✔ Development of secondary sexual characteristics (breast, female body type).
✔ Strengthen bones (prevents osteoporosis).
✔ It affects the skin and hair (increases collagenCollagen is a fibrillar protein, one of the main building elements of the body. It constitutes a significant part of connective tissues such as skin, tendons, joints, bones, and cartilage. Collagen provides strength, elasticity, and structural integrity to these tissues, giving them the ability to resist stretching., hydration).
✔ Pregnancy Support -prepares the uterus for implantation.
Progesterone is a hormone of the yellow body of the ovaries and placenta (during pregnancy).
Functions:
✔ Preparation of the endometrium for implantation of a fertilized egg.
✔ Reduced uterine tone (prevents miscarriage).
Suppressing ovulation in the second phase of the cycle and during pregnancy.
✔ Effect on the mammary glands (preparation for lactation).
| Cycle phase | Norm (pg / ml) | Norm (pmol / l) |
|---|---|---|
| Follicular (1-14 days) | 20–150 | 70–550 |
| Ovulation (~day 14) | 100–400 | 370–1470 |
| Luteal acid(15-28 days) | 50–220 | 180–800 |
| Menopause | <20 | <70 |
| Cycle phase | Norm (ng / ml) | Norm (nmol / l) |
|---|---|---|
| Follicular | 0.1–0.8 | 0.3–2.5 |
| Ovulation | 0.1–1.5 | 0.3–4.8 |
| Luteal acid | 2–25 | 6–80 |
| Menopause | <0.1 | <0.3 |
| Pregnancy (I trimester) | 10–44 | 30–140 |
| Deficiency (hypoestrogenism) | Excess (hyperestrogenism) |
|---|---|
| влагали Vaginal dryness, painful sex | ✅ Breast swelling and swelling |
| Hot flashes, sweating (menopause) | ✅ Increased anxiety |
| ✅ Brittle bones (osteoporosis) | ✅ Migraines, PMS |
| ✅ Dry skin, wrinkles | Fibrocystic mastopathy |
| цикла Cycle disorders (amenorrhea) | ✅ Risk of endometriosis, fibroids |
Causes of the deficit:
Causes of excess:
| Deficit | Excess |
|---|---|
| ✅ Irregular monthly periods | ✅ Drowsiness, fatigue |
| Infertility, miscarriages | ✅ Vertigo |
| ✅ PMS (irritability) | ✅ Decreased libido |
| ✅ Dry skin, hair loss | ✅ Hypotension (low blood pressure) |
Causes of the deficit:
Causes of excess:
Additional tests:
Estradiol – the hormone of femininity, affects the cycle, skin, bones.
✅ Progesterone is a pregnancy hormone that protects against miscarriages.
The norms depend on the phase of the cycle (especially the luteal peak of progesterone is important).
An imbalance leads to PMS, infertility, and early aging.
Correction – diet, HRT, stress reduction.