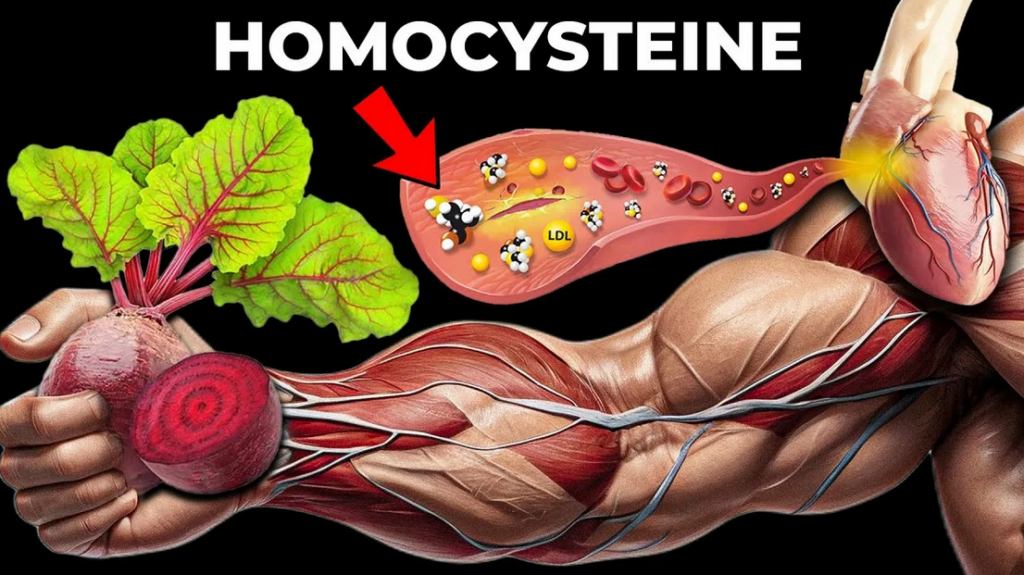
Homocysteine is a sulfur-containing aminoacid, an intermediate product of methionine metabolism (comes from protein foods). Its key functions are:
| Group | Normal Range (µmol/L) |
|---|---|
| Adults | 5–15 |
| Pregnant Women | < 10 |
| Children | < 5 |
Risk thresholds:
It is rare and has no clinical significance.
Possible reasons:
Important: Homocysteine is not tested in isolation – it is checked together with vitamins B9, B12, creatinine, and lipidogram.
Example:
Homocysteine 25 mmol / l + low B12 → methylcobalamin administration → control after 3 months.