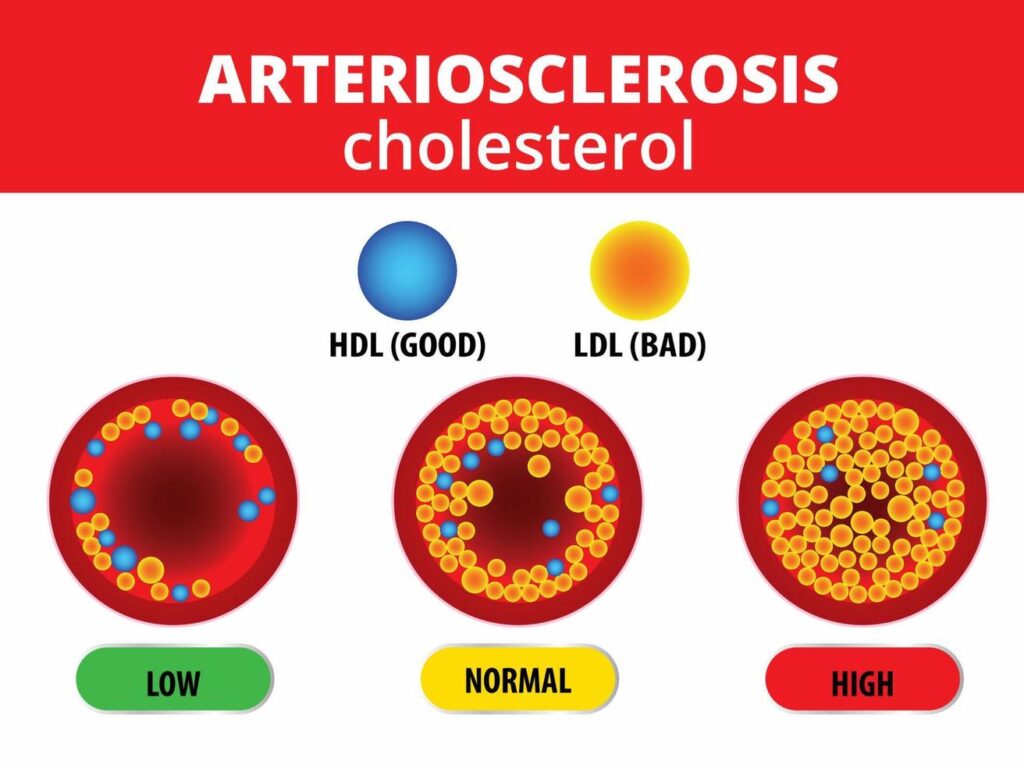
HDL (‘good cholesterol’) – these are lipoproteins that remove excess cholesterol from blood vessels and tissues, transporting it to the liver for processing and elimination.
| Category | Normal HDL (mmol/L) | Normal HDL (mg/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| Men | > 1.0 | > 40 |
| Women | > 1.2 | > 46 |
| Ideal Level (reduces atherosclerosis risk) | > 1.6 (men), > 1.8 (women) | > 60 |
The optimal values depend on gender and the risk of cardiovascular diseases:
Note: The higher the HDL, the better the protection against atherosclerosis.
Low HDL levels (<1.0 mmol/L in men, < 1.2 mmol/L in women) increase the risk:
Very high HDL (> 2.3 mmol / L or > 90 mg / dl) is usually beneficial, but in rare cases may be associated with:
The paradox: In some cases , very high HDL (above 3.0 mmol / L) can lose protective properties and even increase the risk of atherosclerosis due to particle dysfunction.
Physical activity -aerobic exercise (running, swimming) increases HDL by 5-10%.
Healthy fats – omega-3 (fish, flaxseed oil), olive oil, avocado.
✅ Quitting smoking increases HDL by 10-15%.
✅ Moderate alcohol consumption (no more than 1 serving per day for women, 2 for men).
Avoid trans fats(fast food, margarine) and excess fast carbs.