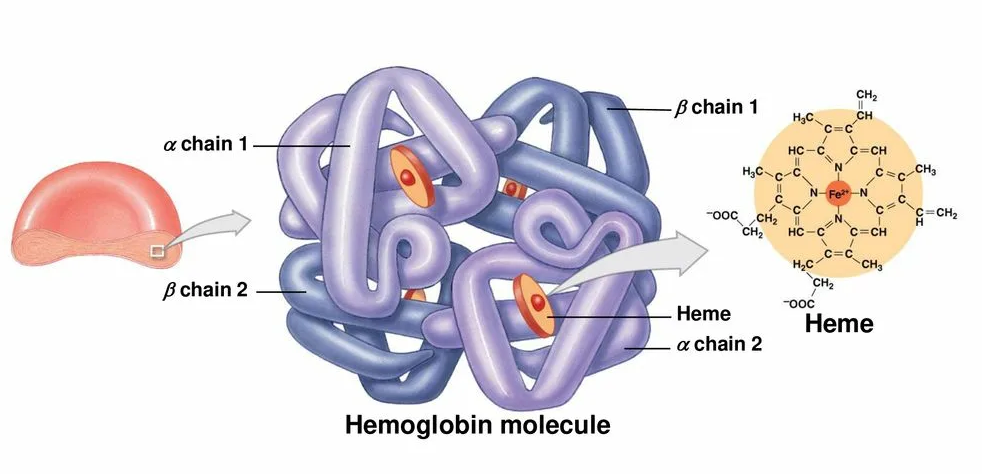
Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein in red blood cells that is responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and removing carbon dioxide.
| Group | Normal Hb (g/L) | Normal Hb (g/dL) |
|---|---|---|
| Men | 130–160 | 13.0–16.0 |
| Women | 120–150 | 12.0–15.0 |
| Pregnant Women | ≥110 | ≥11.0 |
| Children (1–6 years) | 110–140 | 11.0–14.0 |
| Adolescents (12–18 years) | 120–160 | 12.0–16.0 |
The values depend on age and gender:
Note: Smokers and residents of the highlands may have higher Hb than normal.
Reasons:
Clinical manifestations:
Reasons:
Clinical manifestations:
With anemia:
With erythrocytosis: