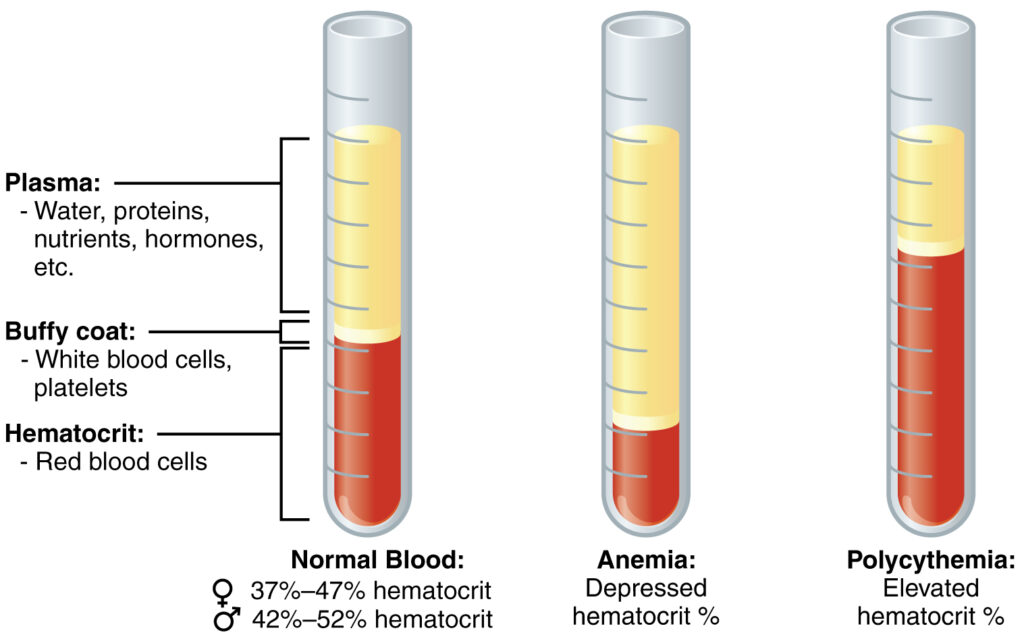
Hematocrit (Hct – Hematocrit) is an indicator that reflects the proportion of red blood cells in the total blood volume. .It helps to assess the density of blood and the ability to transport oxygen.
| Group | Normal (%) |
|---|---|
| Men | 40 – 54 |
| Women | 36 – 48 |
| Children | 32 – 44 |
| Newborns | 45 – 65 |
The values depend on age and gender:
Note: References may vary slightly between laboratories.
Reasons:
Symptoms:
Reasons:
Symptoms: