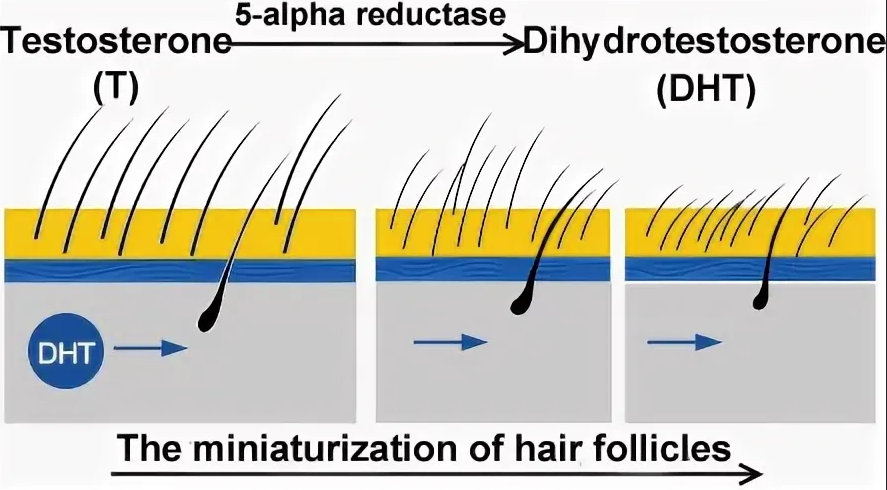
Dehydrotestosterone (DHT) is an active metabolite of testosteroneproduced by the enzyme 5– alpha reductase. . It binds to androgen receptors 3-10 times more strongly than testosterone, and plays a key role in:
The level of DHT is measured in the blood (less often-in tissues).
| Type of analysis | Standards (depending on the laboratory) |
|---|---|
| Men | 250-990 pg / ml (0.25-0.99 ng / ml) |
| Women | 24-450 pg / ml (0.024-0.45 ng / ml) |
| Children (up to puberty) | < 50 pg / ml |
Note:
A rare condition, most often associated with a genetic defect in 5-alpha reductase.
Reasons:
Reasons:
Example: If a woman has DHT &> 500 pg / ml + hirsutism – PCOS or adrenal tumor should be excluded.