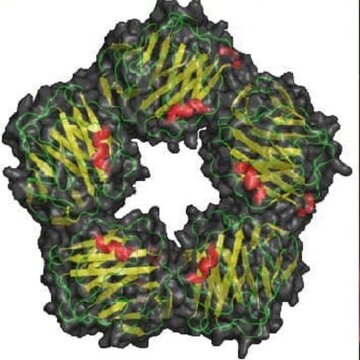
CRP is an acute inflammatory protein produced by the liver in response to an infection, injury, or autoimmune process. It plays a key role in activating the immune systemby binding to pathogens and damaged cells to mark them for destruction.
| Category | Level (mg/L) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy Individuals | < 5 | Normal |
| Mild Inflammation | 5–10 | Possible chronic infection, smoking |
| Moderate Inflammation | 10–50 | Bacterial infections, exacerbation of autoimmune diseases |
| Severe Inflammation | > 50 | Acute bacterial infections, sepsis, burns, trauma |
| hs-CRP (Cardiac Risk) | < 1 | Low risk |
| 1–3 | Moderate risk | |
| > 3 | High risk of atherothrombosis |
Note:
Reasons:
Symptoms of excess:
Depend on the underlying disease:
How dangerous is it?
CRP deficiency is an extremely rare condition, as it can normally be close to zero in healthy people.
Possible causes of artificial decline:
Symptoms of deficiency:
Non-specific, related to the underlying disease:
How dangerous is it?
Low CRP is not an independent pathology, but it can mask inflammation.
A doctor (general practitioner, rheumatologist, infectious diseases specialist) should prescribe and interpret the analysis.