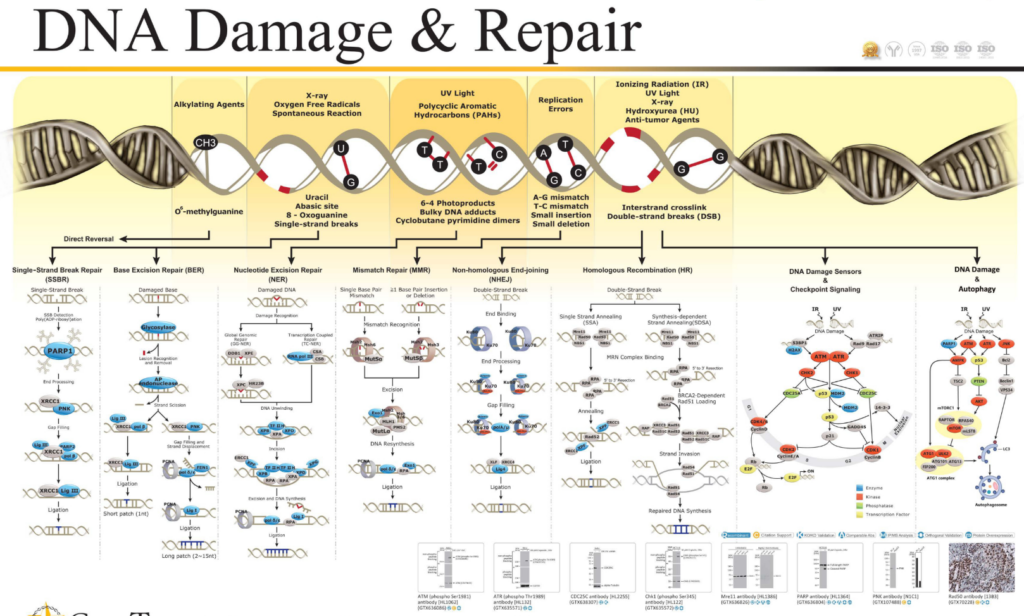
There are laboratory methods to assess the degree of DNA damage*and the effectiveness of DNA repair. These tests are most commonly used for scientific, clinical, or biohacking purposes and are not available in every commercial lab, but they do exist. Below are the main methods:
Анализ Assays and methods for assessing DNA damage
One of the most well-known methods for assessing DNA breaksin individual cells (more often-white blood cells). The test cells are electrophoresized, and the damaged DNA is ‘stretched’, resembling a comet. Allows you to distinguish between single-and double-stranded breaks, as well as oxidative damageto DNA.
Доступность Availability: most often — in scientific / research centers, sometimes-in private clinics on request.
One of the most well-known biomarkers of oxidative DNA damage.
It is a modified form of guanine that occurs when free radicals attack.
Measured in:
Urine— as a systemic marker of DNA damage. Serumor plasma — less sensitive, but possible.
Sometimes-in cells (neutrophils, lymphocytes).
Доступность Availability: Available in some functional labs, sometimes as part of anti-age or detox panels.
Marker of double-stranded DNA breaks.
This is the phosphorylated form of the H2AX protein, which accumulates at the sites of damage.
It is used in scientific and clinical research, for example, in cancer therapy or radiation exposure assessment.
Availability: more often in research or cancer centers, rarely in routine practice.
Measures the appearance of small nuclei*(micronuclei) that are formed from fragments of damaged DNA.
It is used to assess genotoxicity and genome instability.
It can be used both in the blood and in epithelial cells (for example, buccal epithelium).
Редко Rarely available in commercial laboratories, but used in research projects.
Examines the body’s ability to repair damaged DNA.
Methods vary and often require in vitroIn vitro can be defined as in a test tube, outside a living organism. This term is used in scientific research when experiments are conducted in an artificially created environment that mimics the conditions of a living organism. cell culture.
Includes tests for the expression of BRCA1/2, ATM, MSH2, and other genes.
Often — within the framework of genetic or oncological panels, or when hereditary syndromes are suspected.
Study of genes involved in DNA repair:
BRCA1 / 2
ATM
MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 (mismatch-repair system)
XRCC1, OGG1, XPA, etc.
This is not a test for current damage, but an assessment of risk and’ weak spots ‘ in the genome.
If you want practically affordable tests, here’s what you can take:
| Test | Purpose | Where to Find |
|---|---|---|
| 8-OHdG in Urine or Blood* | DNA damage by free radicals | Functional or biohacking laboratories |
| Genetic Test for BRCA, MTHFR, ATM, etc.* | Vulnerability to DNA damage, cancer risk | Genotek, Atlas, Invitro (partially) |
| Glycated AlbuminOne of the main proteins of the human body, responsible for maintaining normal blood composition and transporting various substances throughout the body. It also serves as a reserve source of amino acids. Albumins perform two very important functions: managing the distribution of water within the body, helping the blood transport vitamins, minerals, and medications. They are responsible for water exchange — they help retain it in the vessels and prevent it from excessively moving into the tissues (thus preventing the development of edema). Albumins influence the formation of tissue fluid, urine, and lymph, and also control the process of water absorption from the intestines., Homocysteine, CRP* | Indirect markers of oxidative stress | Any major laboratory |
| Micronucleus Test* | Genomic instability | Only in research institutes/centers |