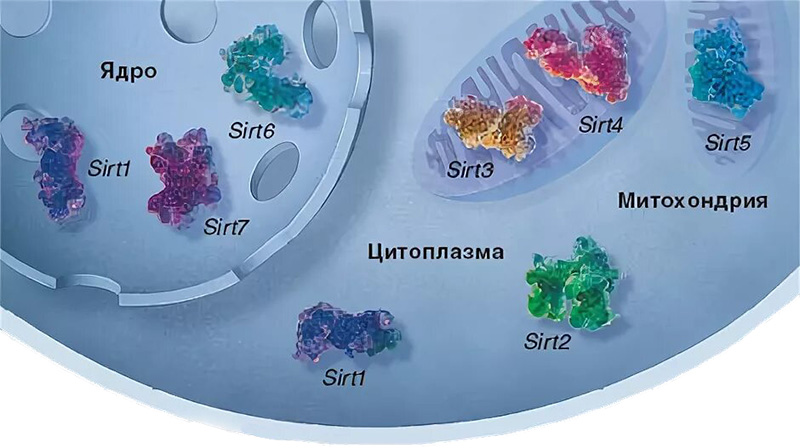
Activation of the SIRT6 gene (sirtuin 6) is of great interest to science and medicine, as this gene plays a key role in regulating a variety of biological processes, including aging, metabolism, DNA repair, and inflammation. SIRT6 is a NAD+ – dependent deacetylase and mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase, and its activation can have a positive effect on health and life expectancy.
SIRT6 activation is actively studied in preclinical and clinical studies. For example: