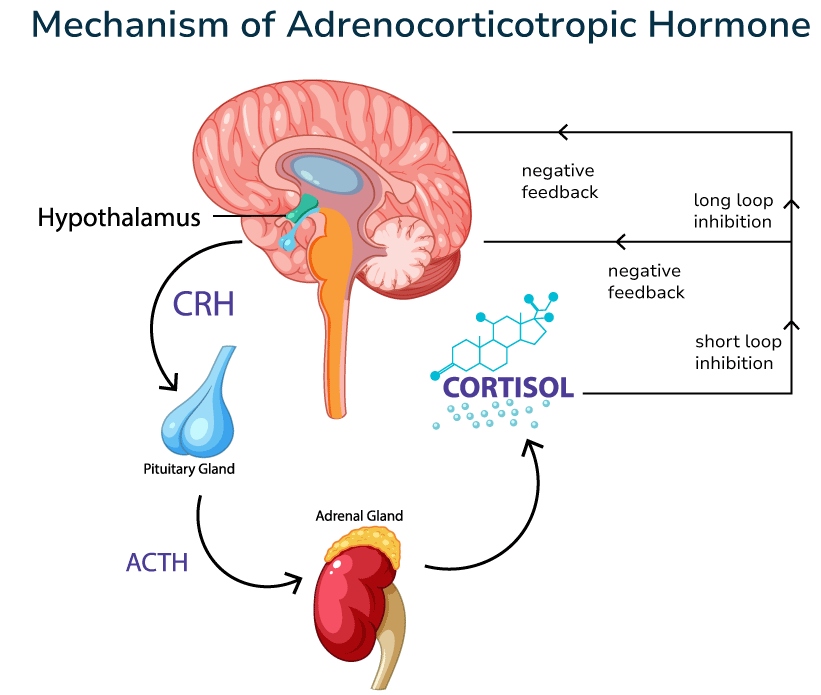
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) is a hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland under the control of the hypothalamus (via corticoliberin, CRH).
Main functions:
✔ Adrenal Stimulation – ACTH causes the adrenal cortex to produce:
✔ Maintaining circadian rhythms – ACTH levels are maximal in the morning (6-8 hours) and minimal in the evening.
✔ Participation in the stress response – under stress (physical or emotional), ACTH secretion increases dramatically.
Reasons:
Symptoms:
Reasons:
Symptoms:
ACTH levels fluctuate strongly throughout the day:
| Time to submit the analysis | Reference values (pg / ml) |
|---|---|
| Morning (7: 00-10: 00) | 7-63 (maximum level) |
| Evening (18: 00-22: 00) | < 30 (minimum level) |
Important:
In case of abnormalities , an endocrinologist’s consultation and additional tests (corticoliberin test, pituitary MRI) are required.