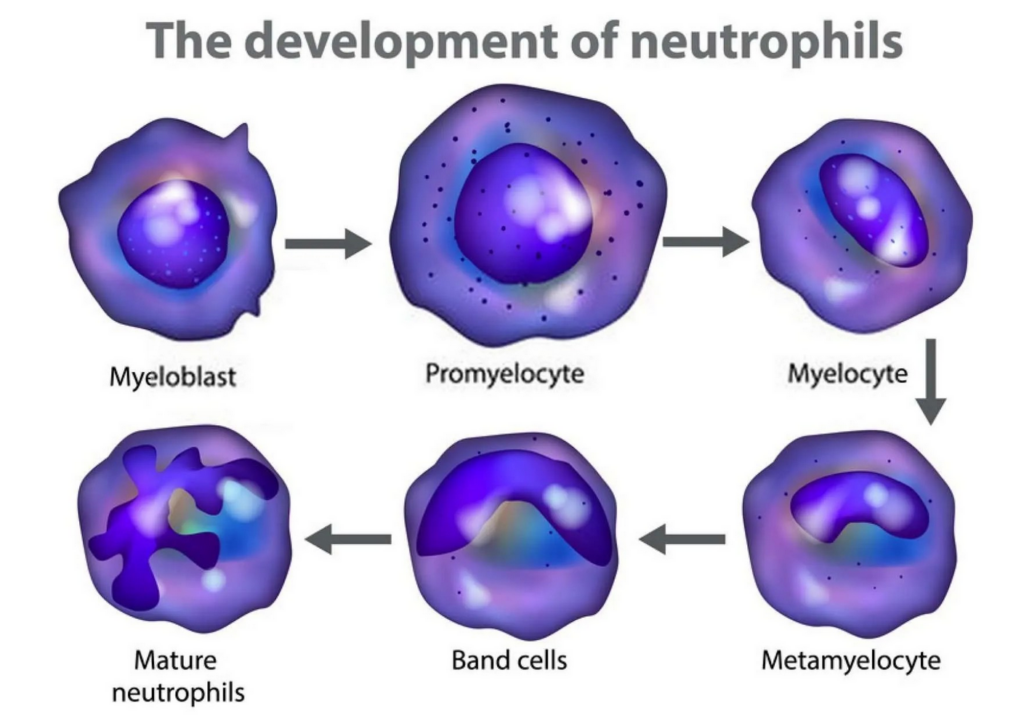
Neutrophils are the most numerous white blood cells (50-75% of all WBC), the main ‘rapid response’ against bacteria and fungi. They are called the ‘first line of defense’.
| Parameter | Absolute value (×10⁹/L) | Percentage of WBC |
|---|---|---|
| Adults | 1.8 – 7.5 | 48–75% |
| Children | 1.5 – 8.5 | 30–60% |
| Newborns | 6.0 – 26.0 | 50–70% |
Note: In pregnant women, an increase of up to 12-14 ×10⁹/l is acceptable.
Critical levels:
Reasons:
Symptoms:
Reasons:
Symptoms:
Depend on the underlying disease:
Important: Neutrophils are the first to react to danger – their fluctuations require a quick diagnosis!